After the payment
Once a payment is made, you can manage it in your Personal Area on Merchant Portal or over the API. Read the sections below to learn more.
Reversal & Refund
If you want to cancel the payment, you can perform one of two operations, depending on the order status: reversal or refund. These operations are described below.
Reversal
Reversal means that the transaction is cancelled and all the funds reserved on the client’s account are released. This operation can be applied to two-phase transactions, when the funds are reserved but not captured yet (Approved status). After the reversal, the transaction gets the Reversed status.
The following ways of reversal are available:
- Reversing a payment on Merchant Portal by clicking the Reverse/Refund button in transaction details. This button works both for reverse and refund depending on the transaction status. Merchant Portal makes a reverse if possible, and if not, makes a refund. Read more here.
Reversing a payment over the API by sending the reverse.do request.
Reversing all two-phase payments automatically after some period. If you need this functionality, contact the support team of the bank.
Reversal can be made only before the end of the current bank day.
Refund
Refund means returning already captured funds to the customer. This operation can be applied to one-phase or two-phase transactions when the funds are already captured (Deposited status). You can make refund more than once, but for a total amount not exceeding the initial captured amount.
The following ways of issuing a refund are available:
- Issuing a refund on Merchant Portal by clicking the Reverse/Refund button in transaction details. This button works both for reverse and refund depending on the transaction status. Merchant Portal makes a reverse if possible, and if not, makes a refund. Read more here.
- Issuing a refund via API by sending the refund.do request.
Both reversal and refund can trigger callback notifications. Read more here.
Getting the order status
You can check the order status at any moment. For example, you may check it after the payment to make sure the order is really paid. The status of the order is available on the Merchant Portal and can also be retrieved over the API.
Looking up the order status on Merchant Portal
You can see the order status in the Transaction details page of the corresponding transaction.
In particular, status Deposited means a succesfull payment.
Getting the order status over the API
The online store sends the getOrderStatusExtended.do request to the Payment Gateway to check the order status. The request contains either orderId (the unique order number in the payment gateway) or orderNumber (the unique order number in the online store’s system). If both parameters are passed to the payment gateway, orderId has higher priority.
The payment gateway returns the order status in the orderStatus parameter. Status 2 means a succesfull payment.
Additional functionality
Two-phase payments
Types of payment
A company may use two types of payments, depending on the specifics of its business:
- One-phase - transactions for payment for goods/services made over the Internet using bank cards that do not require additional confirmation, i.e. holding and debiting of funds takes place in one stage. This type of payments is preferable if the goods or service is provided immediately after payment
- Two-phase - transactions for payment for goods/services made via the Internet with the use of bank cards that require additional confirmation, i.e. payment is made in two stages. At the first stage the check of availability and holding of funds of the payer (pre-authorization) takes place; then, at the second stage, the company either confirms to debit funds, or cancels holding of funds
The amount to be debited may be less than the amount that was held. Debits exceeding the held amount are available as well (with configurable limits). If you need this feature please contact our Support Service.
Two-phase payments should be used if some time elapses between the buyer's decision to pay and delivery of the selected good or service.
For the payment to be a two-phase payment, the order must be registered via registerPreAuth.do request, not register.do.
Two-phase payment is suitable for any method of integration:
For Redirect, Direct, CMS, SDK integration options, it is possible to register and complete an order via API.
Captures
A capture of a pre-authorized amount happens in the second phase of the two-phase payment, when the funds are debited from card holder's account. Once the capture occurs, the order becomes completed and goes in the DEPOSITED status. The amount captured can be greater or less than the pre-authorization amount, and partial capture in increments is available as well. If you do not pass the amount, then the full amount will be executed.
There are three ways to make a capture:
- Capturing a payment on Merchant Portal
- Capturing a payment over the API
- Capturing all two-phase payments automatically after some period
It is available to do a partial capture. It will be less than the order amount and immediately final.
Autocompletion and autoreversal
If you have this feature enabled for you by our support team, you can set up your payment integration so that all preauthorized (Approved) two-phase orders would be completed or reversed automatically after a specific time period. This means that you don't have to process each order manually in the Merchant Portal or to call deposit.do or reverse.do API methods.
To enable order autocompletion via the Merchant Portal:
- Log in to Personal Area.
- In the navigation bar to the left, go to Settings by clicking on the
 icon.
icon. - Go to the General tab.
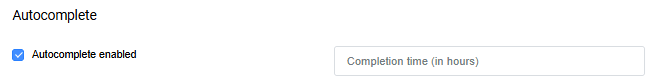
- In the Autocomplete section, select Autocomplete enabled.
- In the Completion time (in hours) field, enter the number of hours after registration, through which a two-phase order should be automatically completed.
It is also possible to enable order autoreversal. In this case, all preauthorized (Approved) two-phase orders will be automatically reversed after a predefined period. Reversal means that the transaction is canceled and all the funds reserved on the client’s account are released.
It is possible to set the date and time of autocompletion and autoreversal via API, by passing the autocompletionDate and autoReverseDate parameters in registerPreAuth.do API request. The used timezone is UTC+3.
Please find below the points describing the logic how autocompletion and autoreversal works.
When the order is registered and autocompletion is set for it:
- If the order status remains Created at the moment the predefined completion starts, no kind of operation will be applied to the order: finally it will expire and be closed. In case the order is deposited after the predefined completion period has passed, the autocompletion won't work.
- If the order is preauthorized and not completed before the predefined completion period, the order will be fully completed, i.e. the preauthorized amount will be automatically deposited in full.
- If the order is preathorized and completed before the predefined completion period, the order status will change according to its normal lifecycle.
- If refund/reverse is applied to the order before the predefined completion period, the autocompletion won't work then.
When the order is registered and autoreversal is set for it:
- If the order status remains Created at the moment the predefined reversal starts, no kind of operation will be applied to the order: finally it will expire and be closed. In case the order is deposited after the predefined autoreversal period has passed, the autoreversal won't work.
- If the order is preauthorized and not completed before the predefined reversal period, the order will be fully canceled, i.e. the preauthorized amount will be automatically reversed in full.
- If the order is preathorized and completed before the predefined reversal period, the order status will change according to its normal lifecycle.
- If refund/reverse is applied to the order before the predefined reversal period, the autoreversal won't work then.
Stored-credential transactions
A stored-credential transaction is used when a cardholder authorizes a merchant to store the payment credentials for further payments. For example, a payer may opt to save their card at checkout. In this case a unique token is generated by the Payment Gateway that links the payer's card number (PAN) to their ID in the store system (for example, to payer's login).
Read about the types of stored credentials supported by the Payment Gateway here.
Storing a credential
You can store a payer's credential via API or via the Merchant Portal UI for any type of integration. See the details below.
Storing a credential upon payment via API
To save a card (create a stored credential) in the Payment Gateway via API, you need to pass the clientId parameter in an order registration or payment initiating request. clientId is an identifier of your client (cardholder), all the client's cards will be attached to this number. For test purposes, you may use any number as clientId. This parameter can be passed in the following requests:
The stored credential will be created only after successful payment. After the payment, you will be able to retrieve the identifier of the stored credential via the getOrderStatusExtended.do request in the bindingId parameter.
To store a credential upon payment via UI
To store a credential upon payment via UI, go to the Personal Area, issue the invoice via the e-mail and make sure to specify the Client ID parameter. As a result, the client will see the Save my card checkbox on the payment page. If the client checks this checkbox, their credential will be stored: the card data will be saved for this client and the client will not have to enter the card data next time. Read more here.
Storing a credential with no charge
If you have this feature enabled for you by our support team, you can store a credential via API with no charge. You can do this by the following ways:
-
Pass the value
VERIFYin thefeaturesblock of any payment request together with theclientIdparameter. In this case, the cardholder will not be charged any amount. The response will contain the identifier of the stored credential in thebindingIdparameter. This binding ID can be used in subsequent requests instead of the saved card details.Read more about the
VERIFYfeature here. Use the createBindingNoPayment.do request.
If you pass the value FORCE_CREATE_BINDING in the features block of the payment request, the credential will be stored forcefully – even if the client has chosen not to save card data on the payment page.
TheFORCE_CREATE_BINDING value cannot be passed in a request with an existing bindingId or bindingNotNeeded = true (will cause validation error). Passing this value also requires passing the clientId parameter.
If both the FORCE_CREATE_BINDING and the VERIFY values are passed in the features block, the order will be created for the purposes of credential storage ONLY (without payment).
Making a stored-credential payment
Stored-credential payments API
Once a credential is stored, you can handle it over the stored-credential payments API (subject to Merchant-level permission). The following methods are available:
- paymentOrderBinding.do – make a stored-credential payment
- getBindings.do – get the list of client's stored credentials
- getBindingsByCardOrId.do – get the list of all stored credentials of a bank card
- unBindCard.do – disable an existing stored credential
- bindCard.do – re-enable an existing stored credential that was disabled
- extendBinding.do – extend a stored credential expiration date
Using stored credentials in recurrent payments
You can use stored credentials for recurring payments. In this case, the bindingId parameter is used in regular order registration request. Read more here.
Using stored credentials in wallet payments
You can also store credentials upon payments via Apple Pay and Google Pay wallets. To do this, pass the clientId parameter in a payment request or in an order registration request (see the description of API requests for wallets).
In this case, a stored credential will link the payer's tokenized card number (DPAN) to their ID in the store system (for example, to payer's login). A credential stored this way cannot be used for displaying a card number on a payment page (because the card number is tokenized). However, this sored credential can be used in recurring payments.
Cardholder verification
Cardholer's card account can be verified without debiting any funds from it. To do this, pass the VERIFY value in the features block of an order registration or payment request.
When the VERIFY feature is used, the payment card will be verified to make sure it is used by its legitimate owner. If 3-D Secure is available for the card, then 3-D Secure verification will be performed. The amount parameter of the verification request can be 0. Even if some amount is passed in the request, no charge will be made. After a successful registration, order status is changed to REVERSED.
If the VERIFY feature is passed together with the clientId parameter, it can be used to store a credential without payment. Read more in the Stored-credential transactions section.
Open ID token
You can generate an Open ID token for a merchant. This token can be used instead of credentials for identifying a merchant in the Payment Gateway.
Open ID token is not private, it can be published or embedded into a web page. For example, it can be used when an order is registered directly from browser. In this case, there is no risk of personal data disclosure, because the token can be interpreted by the Payment Gateway only.
You can use Open ID token for merchant authentication when sending API requests to the Payment Gateway.
To do it, pass the Open ID token in the token parameter instead of passing userName and password. You can use the token parameter in the following requests:
To generate an Open ID token, go to the Personal Area, select Settings on the side menu, and then select General Settings in the Merchant block. Click Generate next to the Open Id token field. If you alredy know your token, you may enter in manually.
Read more here.
Redirect to ACS
Regular redirect
If a payment is made with 3-D Secure, merchants must redirect their customers to ACS using the address specified in the acsUrl parameter received from the payment response. The request body must be MD=mdorder&PaReq=paReq&TermUrl=termUrl, where:
-
MD- unique order ID in the payment gateway; -
PaReq- thepaReqparameter received from the payment response. It is the message that should be sent to ACS together with redirect and contains the data necessary for authentication; -
TermUrl- thetermUrlparameter received from the payment response. It is the URL to which ACS redirects the cardholder after authentication.
It must be a POST request (not GET).
Depending on the configuration agreed with your bank, the customer after ACS authentication will be redirected either to the store or to the payment gateway.
Example of a POST request for regular redirect:
<html>
<head><title>ACS Redirect</title></head>
<body onload="document.forms['acs'].submit()">
ACS Redirect
<form id="acs" method="post" action="[result.acsUrl]">
<input type="hidden" id="MD" name="MD" value="[MD]"/>
<input type="hidden" id="PaReq" name="PaReq" value="[result.PaReq]"/>
<input type="hidden" id="TermUrl" name="TermUrl" value="[result.TermUrl]"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>Regular redirect (advanced 3DS2 scheme)
If 3-D Secure is used, merchants should redirect their clients to the ACS using the address specified in the acsUrl parameter received from the payment response.
The request body must be
creq=[packedCReq] where [packedCReq] is the value of packedCReq parameter received in a response to the second payment request.
It must be a POST request (not GET).
Depending on the configuration agreed with your bank, the customer after ACS authentication will be redirected either to the store or to the payment gateway.
Example of a POST request for regular redirect:
<html>
<head><title>ACS Redirect</title></head>
<body onload="document.forms['acs'].submit()">
ACS Redirect
<form id="acs" method="post" action="[acsUrl]">
<input type="hidden" id="creq" name="creq" value="[packedCReq]"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>Simplified redirect
Alternatively, the online store can use the gateway acsRedirect method, which will perform the same cardholder redirect to the issuer ACS.
Payment with your own 3DS Server
3DS Server is a component of 3D Secure technologies that may be implemented in the payment gateway or on your side. If you have your own 3DS Server, you can use it for 3D Secure authorization on your side, and then just indicate the fact of such authorization in API requests. To enable this feature, contact our support team.
If you use your own 3DS Server, then in every payment request - paymentOrder, paymentOrderBinding.do - include the following additional parameters in the jsonParams block: eci, cavv, xid, threeDSProtocolVersion, and authenticationTypeIndicator. These parameters are described below.
eci
eci parameter - Electronic commerce indicator (ECI) received from your 3-D Secure Server. It shows the security level ensured during payment. The DS server sets this parameter based on the authentication results and in accordance with the features of the merchant verification process. This parameter is passed in jsonParams block in two-digit format, e.g. "eci": "02".
ECI codes may differ depending on the payment system. The most commonly used ECI codes are given below:
| Value | VISA | Mastercard | CUP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Authentication attempt | ||
| 02 | Authentication, full 3DS | Authentication, full 3DS | |
| 05 | Authentication, full 3DS | ||
| 06 | Authentication attempt | ||
| 07 | SSL authentication (without 3DS) | SSL authentication (without 3DS) | |
| 09 | Authentication attempt | ||
| 10 | SSL authentication (without 3DS) |
cavv, xid
If ECI value differs from the ones used for SSL authorizations, it is also necessary to pass the following parameters:
-
cavv- cardholder authentication value; -
xid- identifier of the 3DS authentication transaction of the cardholder on the 3DS server (ARes.dsTransIDvalue received from ACS).
threeDSProtocolVersion
Additionally, you can pass the threeDSProtocolVersion parameter (version of 3DS protocol) in a payment request. It can take the following values:
-
2.1.0- for 3DS 2 -
2.2.0- for 3DS 2
If threeDSProtocolVersion is not passed in the request, then its default value is assumed to be 2.1.0 - for 3DS 2.
authenticationTypeIndicator
authenticationTypeIndicator parameter (payment authentication type) is required for payment via your own 3DS Server with 3DS 2.
For payments with 3DS 1 or SSL, this parameter is optional and is defined automatically depending on ECI value.
| Value | Description | Required/Automatically defined |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | SSL authentication | ECI = 07 |
| 1 | SCA Cardholder authentication with 3DS 1 | ECI = 02, 05 |
| 2 | Cardholder authentication attempt with 3DS 1 | ECI = 01, 06 |
| 3 | SCA Cardholder authentication with 3DS 2 | Required for 3DS 2 |
| 4 | RBA Cardholder authentication with 3DS 2 | Required for 3DS 2 |
| 5 | Cardholder authentication attempt with 3DS 2 | Required for 3DS 2 |
| 6 | 3DS 2 exemption granted | Required for 3DS 2 |
| 7 | 3RI authentication with 3DS 2 | Required for 3RI |
| 8 | 3RI authentication attempt with 3DS 2 | Required for 3RI |
Request example
curl --request POST \\
--url https://3dsec.berekebank.kz/payment/rest/paymentorder.do \\
--header 'content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \\
--data userName=test_user \\
--data password=test_user_password \\
--data MDORDER=0140dda0-71ed-7706-a61f-36bd00a7d8c0 \\
--data '$PAN=4000001111111118' \\
--data '$CVC=123' \\
--data YYYY=2030 \\
--data MM=12 \\
--data 'TEXT=TEST CARDHOLDER' \\
--data language=en \\
--data 'jsonParams={
"eci": "02",
"cavv": "AkZO5XQAA0rhBxoaufa+MAABAAA=",
"xid": "5010857f-8d3f-74e1-9c5a-54a000cc4110",
"threeDSProtocolVersion": "2.2.0",
"authenticationTypeIndicator": "5"
}'If you use your own 3DS Server, the corresponding payment response does not contain 3D Secure-related parameters, such as redirect, termUrl, acsUrl, and paReq.
Response example
{
"redirect": "https://3dsec.berekebank.kz/payment/merchants/temp/finish.html?orderId=01493844-d4d3-703f-9f7e-a73900a7d8c0&lang=en",
"info": "Your order is proceeded, redirecting...",
"errorCode": 0
}3-D Secure authorization
What is 3-D Secure
3-D Secure (also called 3DS) is a technical standard created by Visa and MasterCard that allows you to perform additional authorization of the cardholder on the side of the issuing bank. In order to complete an online purchase, the cardholder is asked to provide proof of identity by entering a unique password, an SMS code, or a temporary PIN.
The term 3DS stands for 3 Domain Server. This name is used because every 3-D Secure transaction involves three parties:
- Acquirer domain. It acts as a 3DS requestor – initiator of authorization process.
- Issuer domain. It includes ACS (Access Control Server) that ensures validation of the payer by the issuing bank.
- Interoperability domain. It acts as a connector between first two domains. Usually, it is a payment system.
Protocol versions
Payment gateway supports 3-D Secure authorization to protect you and your clients from the threat of payment fraud.
For browser-base transactions, we use 3-D Secure v2 (also called 3DS2) – the updated version of 3-D Secure protocol that allows better information exchange between the three parties of the transaction. The 3DSv2 authentication Protocol, depending on the issuing Bank's ACS settings, allows you to perform authentication check without the customer's participation (Frictionless authentication). In this case, the customer will not be required to perform authentication actions, such as entering a one-time password or performing additional authentication checking actions.
Integration scenarios
If the payment page is on the payment gateway side, the merchant does not need any additional actions and can use the standard payment gateway API for integration.
If the payment page is on the merchant's side, when using 3-D Secure authorization, the merchant must send a number of additional API requests to the payment gateway.
See the integration schemes.
3RI authorization
3RI is a type of 3DS 2 authorization that is initiated by the merchant without requesting a cardholder to confirm payment. Actually, 3RI payment is a MIT payment with tii=R or tii=I, i.e. recurrent payment or installment payment (see Transaction types for details) with frictionless 3DS 2 authorization.
3RI recurrent or installment payment is possible only if the initial transaction that stores the credential was performed with 3DS 2 authorization.
If any of the following conditions takes place:
- initial transaction was performed not via the Payment Gateway,
- initial transaction was performed with your own 3DS Server,
- initial transaction was performed without storing credentials,
then you should pass the following additional parameters in jsonParams block:
| Required | Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandatory | initThreeDSReqPriorAuthData | String | Identifier of the initial transaction in DS (dsTransId). Example: "d5bf7963-e94e-718d-8777-2943091ceaa0". |
| Mandatory | initThreeDSReqPriorAuthMethod | String | Authentication method used in initial transaction. Example: "01". |
| Mandatory | initThreeDSReqPriorAuthTimestamp | String | Data and time (UTC) of the initial transaction. Example: "22202405140811". |
| Mandatory | initThreeDSReqPriorRef | String | Additional information for ACS (acsTranId). Example: "d5bf7963-e94e-718d-8777-2943091ceaa0". |
| Conditional | installments | String | Maximum number of allowed authorizations for installment payments. Is required for installment 3RI payment. |
| Conditional | totalInstallmentAmount | String | Total sum of all installment payments. Is required for installment 3RI payment. |
| Mandatory | recurringExpiry | String | The date after which authorizations are not allowed, in YYYYMMDD format. Is required for recurrent or installment 3RI payment. |
| Mandatory | recurringFrequency | String | Minimum number of days between authorizations. Is required for recurrent or installment 3RI payment. |
